Reaction chemistry of CO₂ absorption
The removal of CO2 is required in many applications. Eastman AdapT solvents rely on the chemistry of different amine-CO2 reactions to optimize the performance for each application.
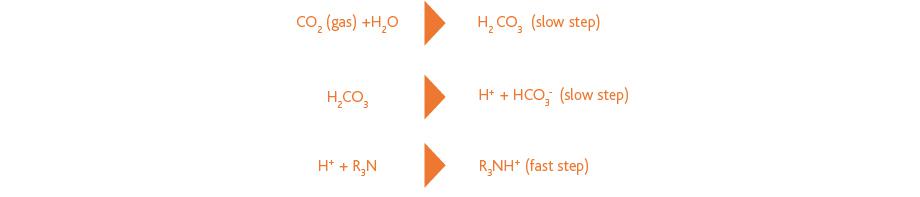
Tertiary amines, such as MDEA, form a bicarbonate with CO2, which is slowly formed in the amine solution. This is illustrated in the following reaction scheme:
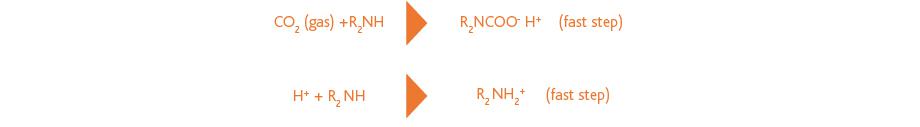
Non-tertiary amines can react much faster with CO2 through formation of a carbamate. The free proton formed in this reaction may protonate a second amine, which is also a fast step, but reduces the absorption capacity. This is illustrated in the following reaction scheme:
Through selection of the type and concentration of the different amines, the CO2 removal rate and absorption capacity can be adapted. In addition to CO2 removal efficiency, system corrosion and operational limitations can also be important factors in solvent selection.